



Calcium Ammonium Nitrate Compared to Calcium Nitrate in Agricultural Applications
Calcium Ammonium Nitrate vs. Calcium Nitrate A Comparative Analysis
In the realm of agriculture, fertilizers play a critical role in enhancing crop productivity and soil health. Among the myriad of options available to farmers, calcium ammonium nitrate (CAN) and calcium nitrate (Ca(NO3)2) are two widely used nitrogenous fertilizers. While they share some similarities due to their calcium and nitrogen content, their chemical compositions, applications, and effects on soil health can lead to different outcomes in agricultural practices.
Chemical Composition and Properties
Calcium ammonium nitrate, as its name suggests, contains both calcium and ammonium. Its chemical formula is typically represented as 5Ca(NO3)2·NH4NO3·10H2O. This compound provides plants with a readily available source of nitrogen in two forms ammonium (NH4+) and nitrate (NO3-). The presence of ammonium can lead to slower leaching rates, making it effective in reducing nitrogen runoff into waterways.
On the other hand, calcium nitrate is purely a calcium and nitrate compound, with its chemical formula being Ca(NO3)2. It is highly soluble in water and provides an immediate source of nitrate nitrogen to the plants. Unlike CAN, it does not release ammonium, which can affect how plants absorb nutrients and interact with soil microorganisms.
Applications in Agriculture
Both fertilizers are utilized in various agricultural settings, but their specific applications can differ based on crop requirements and soil conditions. Calcium ammonium nitrate is often favored for crops that benefit from the dual nitrogen sources, such as cereals, vegetables, and fruits. The ammonium component can be especially beneficial in cool weather as it remains stable in soil.
Calcium nitrate, conversely, is frequently used in soilless cultures and hydroponics systems due to its quick dissolving nature. This makes it an ideal choice for nitrogen-sensitive crops. Its ability to supply calcium also supports strong cell wall development and can help mitigate physiological disorders in crops such as blossom-end rot in tomatoes and peppers.
calcium ammonium nitrate vs calcium nitrate
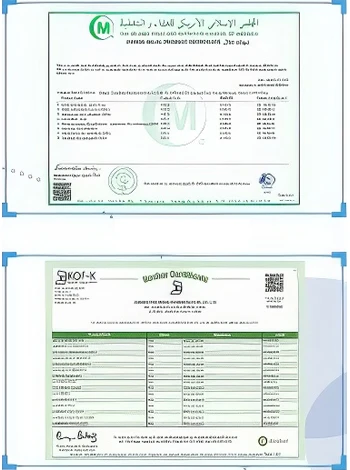
Effects on Soil Health
The choice between calcium ammonium nitrate and calcium nitrate can also affect soil health over time. Calcium plays a crucial role in improving soil structure by promoting aggregation, which enhances water infiltration and aeration. Both fertilizers provide calcium; however, due to the ammonium content in CAN, there may be different impacts on soil pH.
The application of ammonium nitrogen can lead to a temporary decrease in soil pH, resulting in increased acidity levels. This can be both beneficial and detrimental, depending on the specific soil conditions and plant requirements. In contrast, calcium nitrate tends to maintain or even raise soil pH, making it a preferable option for alkaline soils where maintaining pH levels is crucial.
Economic Considerations
From an economic standpoint, the cost and availability of each fertilizer can influence a farmer's choice. CAN typically has a higher price point due to its composite nature, while calcium nitrate, being a more straightforward compound, may offer a more cost-effective solution in certain situations. Farmers often weigh the immediate costs against the long-term benefits in terms of yield and soil health when making this decision.
Conclusion
In summary, both calcium ammonium nitrate and calcium nitrate serve as valuable tools in the agricultural toolbox, each with its unique set of benefits and drawbacks. The choice between these fertilizers should be guided by the specific needs of the crop, soil health considerations, and economic factors. By understanding the differences in composition, application, and effects on soil, farmers can make informed decisions that enhance productivity and sustainability in their agricultural practices. Ultimately, effective fertilizer management can lead to healthier crops, better soil, and more sustainable farming systems.
-
Why Sodium Persulfate Is Everywhere NowNewsJul.07,2025
-
Why Polyacrylamide Is in High DemandNewsJul.07,2025
-
Understanding Paint Chemicals and Their ApplicationsNewsJul.07,2025
-
Smart Use Of Mining ChemicalsNewsJul.07,2025
-
Practical Uses of Potassium MonopersulfateNewsJul.07,2025
-
Agrochemicals In Real FarmingNewsJul.07,2025
-
Sodium Chlorite Hot UsesNewsJul.01,2025










