



use of polyacrylamide
The Use of Polyacrylamide Applications and Benefits
Polyacrylamide, a synthetic polymer, has gained significant attention in various industries due to its versatile properties. Chemically, it is formed from acrylamide monomers, which polymerize to create long chains that can interact with water, other chemicals, and particles. This unique structure allows polyacrylamide to serve multiple purposes in a range of applications, including water treatment, agriculture, and biomedical fields. Understanding its use and benefits can illuminate why polyacrylamide is a valuable material in contemporary practices.
1. Water Treatment
One of the primary uses of polyacrylamide is in water treatment processes. It functions as a flocculant, which means it aids in the clumping together of suspended particles in water. This property is particularly useful in municipal wastewater facilities and industrial effluent management. By enhancing coagulation, polyacrylamide helps to separate solid waste from water, allowing for cleaner discharge into natural water bodies or reuse in various applications. The efficiency of polyacrylamide in binding particles significantly reduces the cost and complexity of water treatment operations.
Furthermore, polyacrylamide's ability to reduce turbidity makes it invaluable in the clarification of drinking water. By improving the sedimentation rates of impurities, it facilitates faster and cleaner water purification processes. This not only ensures compliance with health standards but also helps conserve water resources by enabling the recycling of treated wastewater.
2. Agriculture
In agriculture, polyacrylamide is widely used to improve soil conditions and enhance crop production. As a water-retaining agent, it helps prevent soil erosion and increases the moisture-holding capacity of agricultural lands. This is particularly beneficial in arid and semi-arid regions where water scarcity poses a significant challenge to farming.
The polymer's capacity to form a gel-like structure upon absorbing water allows it to release moisture gradually to the plant roots. This slow release ensures that crops receive a steady supply of water, reducing the frequency of irrigation and promoting efficient water use. Farmers report increased crop yields and improved soil health due to the application of polyacrylamide, highlighting its potential to support sustainable agricultural practices.
use of polyacrylamide
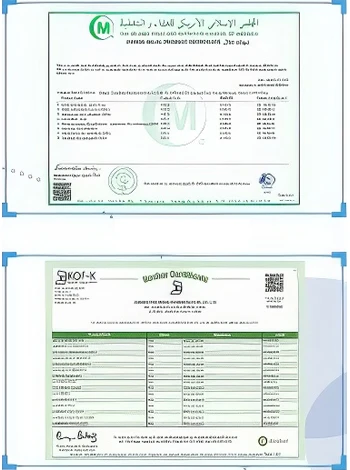
3. Biomedical Applications
Polyacrylamide has also carved out a niche in biomedical applications, particularly in the production of hydrogels. These hydrogels are widely used in drug delivery systems, wound care, and tissue engineering. Their biocompatibility ensures that they can interact safely with biological tissues, making them ideal for medical applications.
In drug delivery, polyacrylamide-based hydrogels can encapsulate pharmaceuticals, allowing for controlled release over time. This targeted delivery reduces side effects and maximizes therapeutic efficacy. In wound care, polyacrylamide hydrogels provide a moist environment that promotes healing while preventing infection. Additionally, in tissue engineering, they serve as scaffolds that support cell growth and tissue regeneration.
4. Environmental Protection
The environmental benefits of polyacrylamide usage cannot be overstated. Its application in soil erosion control and water conservation contributes to sustainable environmental practices. By minimizing runoff and protecting water bodies from contamination, polyacrylamide plays a role in environmental preservation. Additionally, the polymer’s use in capturing pollutants from industrial effluents aids in reducing environmental health risks.
However, it is essential to consider the environmental impact of polyacrylamide itself. While it is generally considered safe in its applications, concerns have been raised regarding the potential toxicity of acrylamide, a monomer from which polyacrylamide is derived. Safe handling and disposal practices must be in place to minimize any adverse effects on health and the environment.
Conclusion
The versatility of polyacrylamide makes it an invaluable asset across various sectors. Its applications in water treatment, agriculture, and biomedical fields showcase its ability to enhance efficiency, promote sustainability, and support innovation. As industries look towards sustainable solutions in an era of environmental consciousness, polyacrylamide demonstrates a promising path forward. The ongoing research and development surrounding this polymer may unlock even more potential benefits, ensuring its place as a critical material in the future.
-
Why Sodium Persulfate Is Everywhere NowNewsJul.07,2025
-
Why Polyacrylamide Is in High DemandNewsJul.07,2025
-
Understanding Paint Chemicals and Their ApplicationsNewsJul.07,2025
-
Smart Use Of Mining ChemicalsNewsJul.07,2025
-
Practical Uses of Potassium MonopersulfateNewsJul.07,2025
-
Agrochemicals In Real FarmingNewsJul.07,2025
-
Sodium Chlorite Hot UsesNewsJul.01,2025










